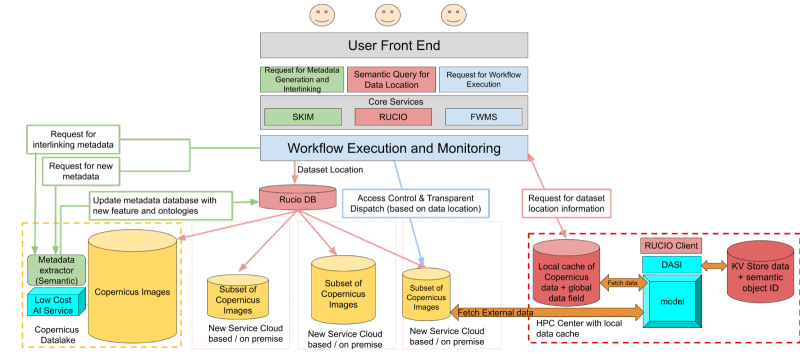
1. Advanced AI techniques for feature extraction from Copernicus Images
Relevance to Work Programme:
From the call: “Copernicus is producing increasingly large data volumes that require specific Big-Data technologies and AI methods to analyze it and manage it.”
Context:
With AI algorithms, it is possible to automatically extract semantic features (metadata) such as land cover, vegetation, water bodies, and urban areas from raw image data. However, Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) of traditional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) used for feature extraction may have limitations in handling larger amounts of data and require ever-increasing computation, leading to reduced efficiency and accuracy. The AI market is reaching maturity and consequently specialized processing architectures are emerging, among them several novel non-Von Neumann (GRAPH’s IPU, Neuromorphic) are reaching the market and are raising high expectations.
Means to Achievement:
DaFab aims to develop real-world prototypes to validate the potential of using these novel processing techniques for feature extraction from Copernicus images. Processor architectures for AI are no longer limited to GPU, IPU and Neuromorphic are emerging as valid alternatives. These designs try to mimic the spatiotemporal modeling of the human brain, and, therefore, more efficient than computing static data,. By using these alternative processor architectures, feature extraction can be done more comprehensively and accurately, even allowing for the processing of the entire Copernicus image archive. More than this, it ensures a higher potential for evolution than the traditional ANNs, which seem to have reached their apogee.